How To Make A Qubit Represent A Probability
Even though probabilities are not what you should care about
Ry-Gate is the direct way to control measurement probabilities. At least, it seems that way. But it is based on a fundamental assumption that, if not met, will break your code.
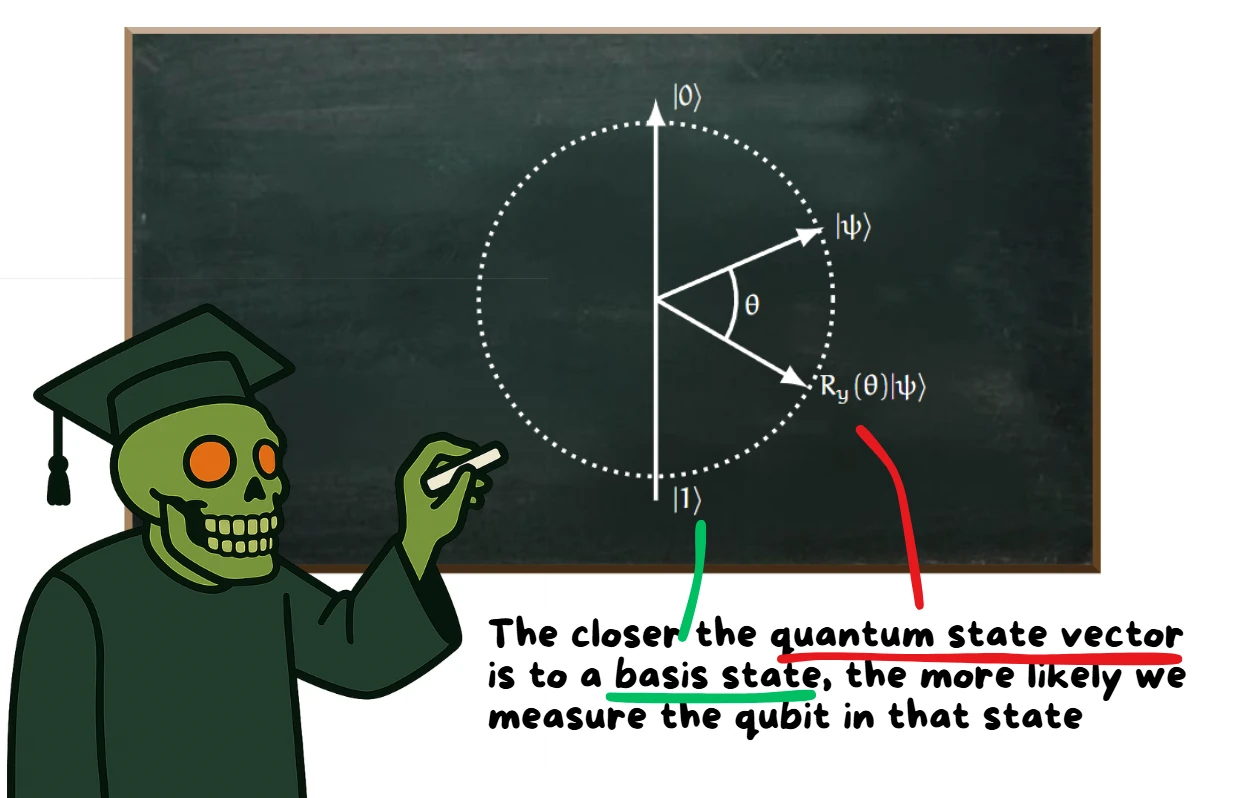
The Ry gate is a single-A qubit is the basic unit of quantum information, representing a superposition of 0 and 1 states.
Learn more about Quantum Bit A quantum gate is a basic operation that changes the state of one or more qubits, similar to how a logic gate operates on bits in classical computing. It uses unitary transformations, meaning it preserves the total probability (the state’s length in complex space). Quantum gates enable superposition and entanglement, allowing quantum computers to perform computations that classical ones cannot efficiently replicate.
Learn more about Quantum Gate that rotates a A qubit is the basic unit of quantum information, representing a superposition of 0 and 1 states.
Learn more about Quantum Bit state around the
Learn more about Amplitude) of measuring
Learn more about
Learn more about
Learn more about Quantum Phase
The above image shows that effect in a two-dimensional representation that omits the A complex number is a number that has two parts: a real part and an imaginary part, written as
Learn more about Complex Number A **quantum phase** is the angle component of a particle’s wavefunction that determines how its probability amplitude interferes with others. It doesn’t affect observable probabilities directly but becomes crucial when comparing two or more states, as phase differences lead to interference effects. Essentially, it encodes the relative timing or “alignment” of quantum waves.
Learn more about Quantum Phase.
The closer the head of the A quantum state vector is a mathematical object (usually denoted |ψ⟩) that fully describes the state of a quantum system. Its components give the probability amplitudes for finding the system in each possible basis state. The squared magnitude of each component gives the probability of measuring that corresponding outcome.
Learn more about Quantum State Vector
Learn more about Basis State
Learn more about
Learn more about
Learn more about Measurement the A qubit is the basic unit of quantum information, representing a superposition of 0 and 1 states.
Learn more about Quantum Bit in that state.
This post is accompanied by a PDF file summarizing the key points.
Rotating the A quantum state vector is a mathematical object (usually denoted |ψ⟩) that fully describes the state of a quantum system. Its components give the probability amplitudes for finding the system in each possible basis state. The squared magnitude of each component gives the probability of measuring that corresponding outcome.
Learn more about Quantum State Vector around the y-axis (which would protrude perpendicularly from the center of the circle) therefore has a direct influence on the In quantum computing, measurement is the process of extracting classical information from a quantum state. It collapses a qubit’s superposition into one of its basis states (usually
Learn more about Measurement probabilities .
? shows how the The Ry gate is a single-qubit quantum gate that rotates a qubit’s state around the Y-axis of the Bloch sphere by a specified angle
Learn more about Ry Gate works in Qiskit is an open-source Python framework for programming and simulating quantum computers. It lets users create quantum circuits, run them on real quantum hardware or simulators, and analyze the results. Essentially, it bridges high-level quantum algorithms with low-level hardware execution.
Learn more about Qiskit
In this code listing, we
- the required functions from
mathand Qiskit, - a
QuantumCircuitinstance (qc) with a single A qubit is the basic unit of quantum information, representing a superposition of 0 and 1 states.
Learn more about Quantum Bit Qiskit is an open-source Python framework for programming and simulating quantum computers. It lets users create quantum circuits, run them on real quantum hardware or simulators, and analyze the results. Essentially, it bridges high-level quantum algorithms with low-level hardware execution.
Learn more about Qiskit initializes A qubit is the basic unit of quantum information, representing a superposition of 0 and 1 states.
Learn more about Quantum Bit in the state, - the angle
thetain radians, - the The Ry gate is a single-qubit quantum gate that rotates a qubit’s state around the Y-axis of the Bloch sphere by a specified angle
. It changes the probabilities (amplitudes) of measuring or without altering their relative phase.
Learn more about Ry Gate with the specified anglethetato the first (and only) A qubit is the basic unit of quantum information, representing a superposition of 0 and 1 states.
Learn more about Quantum Bit at position0of theqc, - the
qcA quantum circuit is a sequence of quantum gates applied to qubits, representing the operations in a quantum computation. Each gate changes the qubits’ state using quantum mechanics principles like superposition and entanglement. The final qubit states, when measured, yield the circuit’s computational result probabilistically.
Learn more about Quantum Circuit into aStatevectorclass instance by using the static methodfrom_instruction.
The Statevector class allows us to analyze the resulting A quantum state vector is a mathematical object (usually denoted |ψ⟩) that fully describes the state of a quantum system. Its components give the probability amplitudes for finding the system in each possible basis state. The squared magnitude of each component gives the probability of measuring that corresponding outcome.
Learn more about Quantum State Vector and reason about its implications, such as its raw data. That is the amplitudes depicted in ?.
We can also a histogram of the In quantum computing, measurement is the process of extracting classical information from a quantum state. It collapses a qubit’s superposition into one of its basis states (usually
Learn more about Measurement probabilities associated with this A quantum state vector is a mathematical object (usually denoted |ψ⟩) that fully describes the state of a quantum system. Its components give the probability amplitudes for finding the system in each possible basis state. The squared magnitude of each component gives the probability of measuring that corresponding outcome.
Learn more about Quantum State Vector resulting in ?.
As we see, rotating the A quantum state vector is a mathematical object (usually denoted |ψ⟩) that fully describes the state of a quantum system. Its components give the probability amplitudes for finding the system in each possible basis state. The squared magnitude of each component gives the probability of measuring that corresponding outcome.
Learn more about Quantum State Vector by
Learn more about Measurement the A qubit is the basic unit of quantum information, representing a superposition of 0 and 1 states.
Learn more about Quantum Bit as
Learn more about
Apparently, since the The Ry gate is a single-qubit quantum gate that rotates a qubit’s state around the Y-axis of the Bloch sphere by a specified angle
Learn more about Ry Gate rotates the A quantum state vector is a mathematical object (usually denoted |ψ⟩) that fully describes the state of a quantum system. Its components give the probability amplitudes for finding the system in each possible basis state. The squared magnitude of each component gives the probability of measuring that corresponding outcome.
Learn more about Quantum State Vector around the
Learn more about Measurement probabilities. So, if what we care about is probability, why not think directly in probabilities and let the angle take care of itself?
In fact, we don't even need to specify the angle
Probabilities come from absolute squared In quantum computing an amplitude is a complex number that describes the weight of a basis state in a quantum superposition. The squared magnitude of an amplitude gives the probability of measuring that basis state. Amplitudes can interfere, this means adding or canceling, allowing quantum algorithms to bias outcomes toward correct solutions.
Learn more about Amplitude The The Ry gate is a single-qubit quantum gate that rotates a qubit’s state around the Y-axis of the Bloch sphere by a specified angle
Learn more about Ry Gate produces real In quantum computing an amplitude is a complex number that describes the weight of a basis state in a quantum superposition. The squared magnitude of an amplitude gives the probability of measuring that basis state. Amplitudes can interfere, this means adding or canceling, allowing quantum algorithms to bias outcomes toward correct solutions.
Learn more about Amplitude with a fixed sine cosine structure. That structure can be inverted exactly. If you want a probability p of In quantum computing, measurement is the process of extracting classical information from a quantum state. It collapses a qubit’s superposition into one of its basis states (usually
Learn more about Measurement
Learn more about
which gives
That single equation turns probability into geometry.
? adds a helper function prob_to_angle that a given real probability value into an equivalent rotation angle.
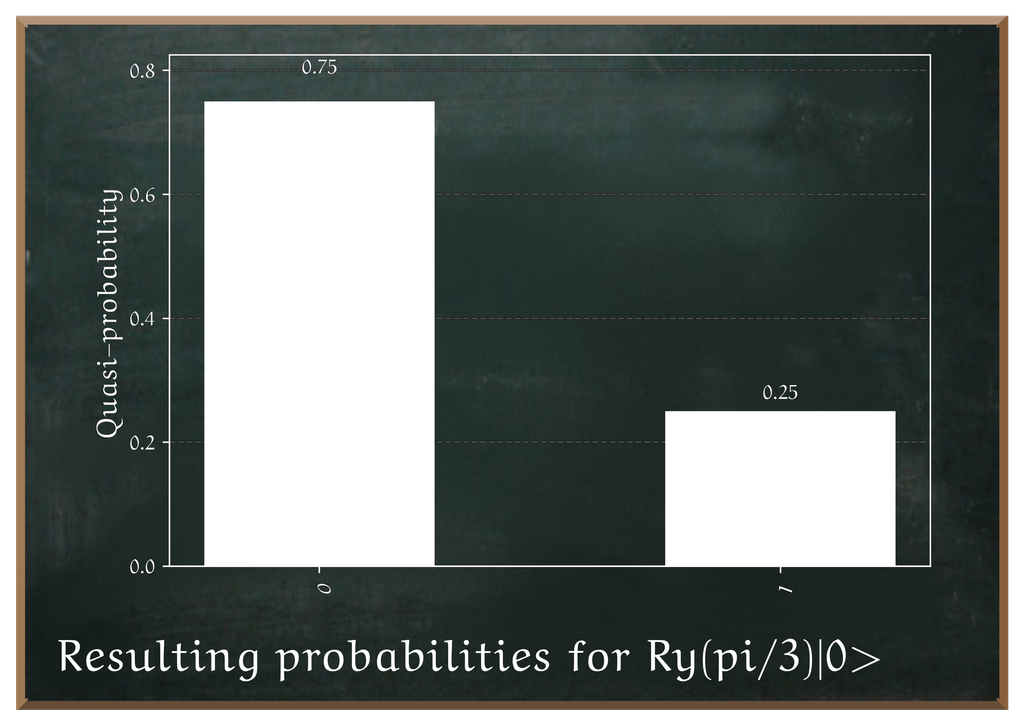
We use the prob_to_angle function to calculate the angle we into the The Ry gate is a single-qubit quantum gate that rotates a qubit’s state around the Y-axis of the Bloch sphere by a specified angle
Learn more about Ry Gate. The result is a A quantum state vector is a mathematical object (usually denoted |ψ⟩) that fully describes the state of a quantum system. Its components give the probability amplitudes for finding the system in each possible basis state. The squared magnitude of each component gives the probability of measuring that corresponding outcome.
Learn more about Quantum State Vector whose In quantum computing, measurement is the process of extracting classical information from a quantum state. It collapses a qubit’s superposition into one of its basis states (usually
Learn more about Measurement probability for 0.6 as the histogram in ? denotes.

Once you have a function that converts probability into an angle, it is tempting to reuse it. If it worked once, it should work again.
However, this calculation of
Learn more about Quantum Bit starts in the state
Learn more about
Learn more about Quantum State is different, the relationship between the angle and probability changes.
That assumption is where things break. You apply one rotation to encode a probability. Then you apply another rotation, computed the same way, to change it. The result is wrong. The histogram jumps somewhere unexpected. It feels like the A qubit is the basic unit of quantum information, representing a superposition of 0 and 1 states.
Learn more about Quantum Bit ignored your instruction. The formula is not wrong. The mental model is. The The Ry gate is a single-qubit quantum gate that rotates a qubit’s state around the Y-axis of the Bloch sphere by a specified angle
Learn more about Ry Gate does not overwrite probabilities. It adds angles.
? shows what happens when we add another The Ry gate is a single-qubit quantum gate that rotates a qubit’s state around the Y-axis of the Bloch sphere by a specified angle
Learn more about Ry Gate.
The The Ry gate is a single-qubit quantum gate that rotates a qubit’s state around the Y-axis of the Bloch sphere by a specified angle
Learn more about Ry Gate rotates the A quantum state vector is a mathematical object (usually denoted |ψ⟩) that fully describes the state of a quantum system. Its components give the probability amplitudes for finding the system in each possible basis state. The squared magnitude of each component gives the probability of measuring that corresponding outcome.
Learn more about Quantum State Vector such that it corresponds to a probability of 0.6 computed by prob_to_angle(0.6).
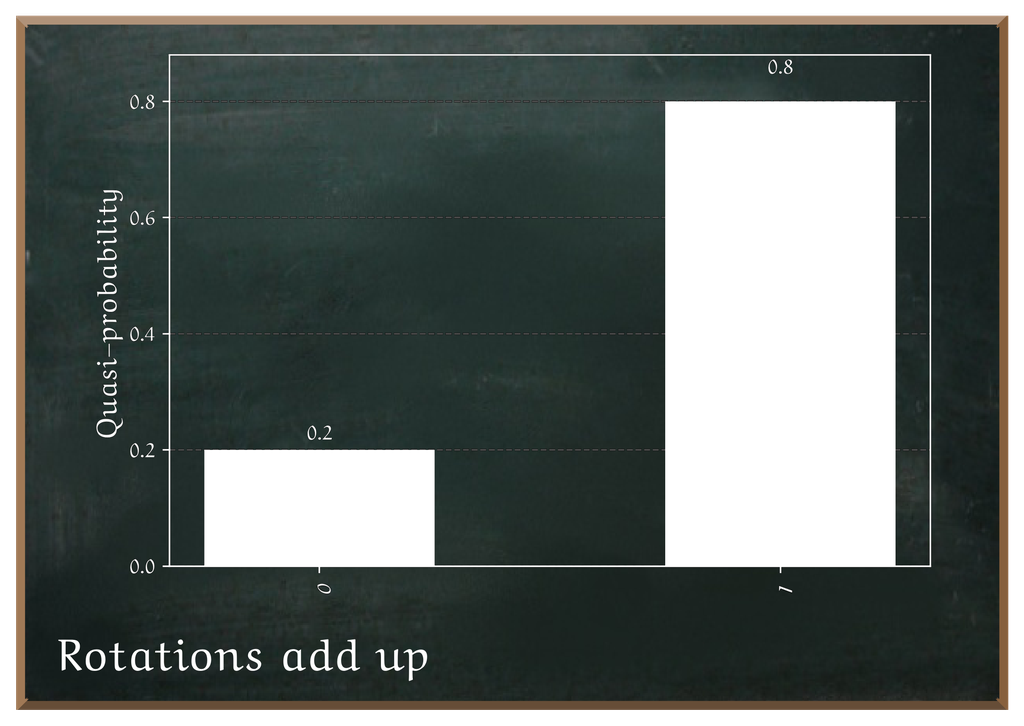
Accordingly, we could assume that a rotation of prob_to_angle(0.2) would result in an overall probability of measuring
This is not the case, though, as ? indicates.

We end up with a probability of
Learn more about Quantum Bit in
The reason for this is that the second
Learn more about Quantum Bit in the state prob_to_angle(p) only works as intended if the input state is exactly
which gives a direct and simple link between the angle
Yet, after the first rotation, the A qubit is the basic unit of quantum information, representing a superposition of 0 and 1 states.
Learn more about Quantum Bit is no longer in
Learn more about Ry Gate mixes these existing amplitudes according to its matrix rule, rather than adding the probabilities linearly.
The call to prob_to_angle(0.2) cannot therefore be interpreted as add
Learn more about Quantum State Vector again, changing the geometry of the state in a nonlinear way. This geometric complication is the reason why the final probability is approximately
In short, each The Ry gate is a single-qubit quantum gate that rotates a qubit’s state around the Y-axis of the Bloch sphere by a specified angle
Learn more about Ry Gate acts on the current In quantum computing an amplitude is a complex number that describes the weight of a basis state in a quantum superposition. The squared magnitude of an amplitude gives the probability of measuring that basis state. Amplitudes can interfere, this means adding or canceling, allowing quantum algorithms to bias outcomes toward correct solutions.
Learn more about Amplitude structure and not on your desired probability target. For this reason, successive rotations can lead to results that appear unexpectedly large from a purely probabilistic point of view.
At this point the A qubit is the basic unit of quantum information, representing a superposition of 0 and 1 states.
Learn more about Quantum Bit is no longer a probability container. It is a point on a sphere with memory. Geometry remembers history. Probability does not. What sounds like a limitation is actually a clue. Every probability corresponds to a unique angle. The current A quantum state is the complete mathematical description of a quantum system, containing all the information needed to predict measurement outcomes. It’s usually represented by a wavefunction or a state vector in a Hilbert space. The state defines probabilities, not certainties, for observable quantities like position, momentum, or spin.
Learn more about Quantum State already has an angle, whether you tracked it or not. Moving from one probability to another is simply moving from one angle to another.
We must include the current In quantum computing an amplitude is a complex number that describes the weight of a basis state in a quantum superposition. The squared magnitude of an amplitude gives the probability of measuring that basis state. Amplitudes can interfere, this means adding or canceling, allowing quantum algorithms to bias outcomes toward correct solutions.
Learn more about Amplitude of the A quantum state vector is a mathematical object (usually denoted |ψ⟩) that fully describes the state of a quantum system. Its components give the probability amplitudes for finding the system in each possible basis state. The squared magnitude of each component gives the probability of measuring that corresponding outcome.
Learn more about Quantum State Vector in the function that calculates
Learn more about Quantum Bit before determining the rotation required to achieve the desired final probability.
The function prob_to_angle_from_old_prob two probabilities as parameters. It assumes that the qubit has already been rotated away from the A basis state in quantum computing is one of the fundamental states that form the building blocks of a quantum system’s state space. For a single qubit, the basis states are
Learn more about Basis State
That means the A qubit is the basic unit of quantum information, representing a superposition of 0 and 1 states.
Learn more about Quantum Bit is in state
Since The Ry gate is a single-qubit quantum gate that rotates a qubit’s state around the Y-axis of the Bloch sphere by a specified angle
Learn more about Ry Gate add their rotation angles when applied in sequence, the total rotation after applying a second The Ry gate is a single-qubit quantum gate that rotates a qubit’s state around the Y-axis of the Bloch sphere by a specified angle
Learn more about Ry Gate will be
The In quantum computing, measurement is the process of extracting classical information from a quantum state. It collapses a qubit’s superposition into one of its basis states (usually
Learn more about Measurement probability for outcome
So, to apply a rotation angle that corresponds to the target_prob, we must subtract the angle that corresponds to the old_prob.
The function implements this idea directly. It the old probability and subtracts it from the target probability. In other terms, the function undoes the first rotation and applies the new. In one single The Ry gate is a single-qubit quantum gate that rotates a qubit’s state around the Y-axis of the Bloch sphere by a specified angle
Learn more about Ry Gate.
? shows the resulting probabilities. It leaves the A qubit is the basic unit of quantum information, representing a superposition of 0 and 1 states.
Learn more about Quantum Bit in a A quantum state is the complete mathematical description of a quantum system, containing all the information needed to predict measurement outcomes. It’s usually represented by a wavefunction or a state vector in a Hilbert space. The state defines probabilities, not certainties, for observable quantities like position, momentum, or spin.
Learn more about Quantum State whose In quantum computing an amplitude is a complex number that describes the weight of a basis state in a quantum superposition. The squared magnitude of an amplitude gives the probability of measuring that basis state. Amplitudes can interfere, this means adding or canceling, allowing quantum algorithms to bias outcomes toward correct solutions.
Learn more about Amplitude correspond to the specified probability.
This looks like bookkeeping, and it is. But that bookkeeping restores predictability. You are no longer fighting the A qubit is the basic unit of quantum information, representing a superposition of 0 and 1 states.
Learn more about Quantum Bit. You are working with its geometry.
In Quantum Computing is a different kind of computation that builds upon the phenomena of Quantum Mechanics.
Learn more about Quantum Computing probabilities are everywhere. Yet, you must remember that you don't work with probabilities directly. Instead, you work with rotation angles.
Rotations accumulate cleanly and reversibly. Probabilities enter only at In quantum computing, measurement is the process of extracting classical information from a quantum state. It collapses a qubit’s superposition into one of its basis states (usually
Learn more about Measurement A A qubit is the basic unit of quantum information, representing a superposition of 0 and 1 states.
Learn more about Quantum Bit does not store probabilities or uncertainty. It stores the A quantum state vector is a mathematical object (usually denoted |ψ⟩) that fully describes the state of a quantum system. Its components give the probability amplitudes for finding the system in each possible basis state. The squared magnitude of each component gives the probability of measuring that corresponding outcome.
Learn more about Quantum State Vector Probability is not written into the A qubit is the basic unit of quantum information, representing a superposition of 0 and 1 states.
Learn more about Quantum Bit It emerges when you look at it. Once you accept that probability is geometry, not noise, the The Ry gate is a single-qubit quantum gate that rotates a qubit’s state around the Y-axis of the Bloch sphere by a specified angle
Learn more about Ry Gate stops being a trick. It becomes a language for saying exactly what you want the A qubit is the basic unit of quantum information, representing a superposition of 0 and 1 states.
Learn more about Quantum Bit to mean.